Home > News > Specials
The Rediff Special/rediff.com Newsdesk
December 01, 2004

 Twenty years after the world's worst industrial disaster killed 7,000 people, maimed thousands for life, and eventually claimed at least 15,000 more lives, the survivors of the Bhopal gas tragedy still await justice.
Twenty years after the world's worst industrial disaster killed 7,000 people, maimed thousands for life, and eventually claimed at least 15,000 more lives, the survivors of the Bhopal gas tragedy still await justice.
Union Carbide Corporation has washed its hands off the case, and the Government of India is not pushing too hard.
So where does that leave the victims?
All they have got to show for their endless padyatras, dharnas and hunger strikes is money from the American multinational that is not enough to even cover their medical bills.
rediff.com presents a ready reckoner to the Bhopal victims' quest for justice:
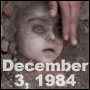
December 2-3, 1984: Methyl isocynate gas leaks from the Union Carbide factory in Bhopal, killing 2,000 people instantly.
December 4, 1984: The Bhopal police files its first information report.
December 7, 1984: Union Carbide Chairman Warren Anderson, the prime accused, and eight others are arrested. Anderson is released on bail of Rs 25,000.
December 1, 1987: The Central Bureau of Investigation files chargesheets against Anderson and 11 others including Union Carbide (USA), Union Carbide (Eastern) Hong Kong, and Union Carbide India Limited, the Indian subsidiary.
Summons are served on Anderson and Union Carbide.
July 6, 1988: The Bhopal chief judicial magistrate issues a non-bailable arrest warrant against Anderson for repeatedly ignoring summons.
February 14-15, 1989: While the issue of interim compensation is being heard before the Supreme Court, Union Carbide and the Indian government strike a deal, under which the company pays a compensation of $470 million. In return, criminal charges are withdrawn against the company.
February-March 1989: The Bhopal Gas Peedith Mahila Udyog Sanghatan, the Bhopal Gas Peedith Sangharsh Sahayog Samiti and other concerned groups file of a number of review and writ petitions in the Supreme Court against the settlement.
October 3, 1991: The Supreme Court revokes criminal immunity granted to Union Carbide and all other accused in response to the review and writ petitions.
The court also orders the government to construct a 500-bed hospital for the victims. Union Carbide and UCIL are asked to pay money to construct the hospital and run it for eight years.
November 11, 1991: Criminal cases against all the accused are revived in the Bhopal court.
January 1, 1992: Proclamation for Anderson's appearance is published in The Washington Post.
February 1, 1992: After ignoring four court summons, Anderson is declared a fugitive. Union Carbide and UCE also are proclaimed absconders.
February 21, 1992: A chief judicial magistrate's proclamation is published in The Washington Post declaring Union Carbide an absconder and ordering it to appear before court on March 27, 1992.
April 30, 1992: The chief judicial magistrate attaches the shares and properties of UCIL held by Union Carbide.
May 22, 1992: The chief judicial magistrate commits the case to trial after separating three of the 12 accused who are proclaimed as absconders -- Anderson, Union Carbide and UCE.
October 1992: The Permanent People's Tribunal on Industrial Hazards and Human Rights holds its session in Bhopal and recommends the setting up of an International Medical Commission on Bhopal.
January 7 to 25, 1994: The IMCB is formed as 14 medical specialists from 11 countries come together to deliberate on the long-term medical care of the victims.
September 1996: The Supreme Court dilutes charges against UCIL's Indian managers, partly on grounds that culpability lies with Union Carbide.
August 1999: Union Carbide announces a merger with Dow Chemical Company.
November 1999: Several individual victims and survivors' organisations file a class action suit against Union Carbide and Anderson in a federal court in New York.
August 2000: Federal Judge John F Keenan dismisses the suit. Lawyers acting for the plaintiffs appeal.
February 2001: Union Carbide merges with Dow Chemicals and Dow claims it is not responsible for a factory it didn't operate.
November 2001: US Second Circuit Court of Appeals reinstates parts of the class action suit.
May 24, 2002: The CBI requests the Bhopal magistrate to dilute the charges against Anderson, from 'culpable homicide' to 'criminal negligence.'
August 28, 2002: The magistrate reaffirms the charges and demands Anderson's extradition.
August 29, 2002: Greenpeace visits Anderson at his home and hands him an arrest warrant.
March 18, 2003: Judge Keenan again throws out the suit.
March 25, 2003: Three survivors' groups hold a press conference in Bhopal and announce that they will appeal the decision.
May-June 2003: The government conveys its request for Anderson's extradition to the US.
October 18, 2003: US Congressmen file an amicus brief with the Second Circuit, Court of Appeals.
March 9, 2004: The Reserve Bank of India through an affidavit confirms that it has more than Rs 1,505 crore (Rs 15.05 billion) left in the compensation fund.
March 17, 2004: The Second Court of Appeals rules that the victims are entitled to pursue claims against Union Carbide.
April, 2004: All the pre-trial hearings in New York are transferred from Judge Keenan's court to Judge Pitman's court.
July 13, 2004: The US government rejects Anderson's extradition request. The rejection is on technical grounds like non-framing of charges against him in Bhopal.
July 19, 2004: The Supreme Court orders the government to distribute the balance of compensation remaining from Union Carbide's settlement amount (Rs 1,503 crores) among the survivors whose claims are settled.
October 26, 2004: The Supreme Court approves a plan for the distribution of Rs 1,567 crores -- Rs 1,503 crores with interest accrued -- among 5.72 lakh victims.